The world of money is changing faster than ever, and cryptocurrency is at the center of that transformation.
In 2025, the global crypto market has surged past $4.3 trillion, with more than 420 million people owning some form of digital currency.
What began as a niche experiment in 2009 has grown into a full-scale financial ecosystem shaping how we invest, trade, and even send money across borders.
So, what exactly is driving this explosive growth?
From Bitcoin’s acceptance as legal tender in El Salvador to the launch of Bitcoin ETFs by giants like BlackRock and Fidelity, institutional adoption is rewriting the rules of modern finance.
Meanwhile, new technologies like decentralized finance (DeFi) and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are connecting traditional systems with the crypto world.
If you’re new to cryptocurrency, this guide is built to help you cut through the noise.
You’ll learn what crypto is, how it works, and how to start investing safely without getting lost in jargon or hype.
Let’s start with the basics: what exactly is cryptocurrency?
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is digital money designed for the internet age.
Unlike traditional currencies like dollars or euros, crypto isn’t issued or controlled by any government or central bank.
Instead, it runs on a technology called blockchain, a public, digital ledger that records every transaction across thousands of computers worldwide.
Each cryptocurrency operates within its own network, secured by cryptography, which protects data and ensures that only the rightful owner can access or transfer funds.
You can think of it as a digital version of cash; you own it directly, without needing a bank or payment company in between.
The first and most famous cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, was created in 2009 by an anonymous figure known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It introduced a revolutionary idea: a financial system built on trustless, peer-to-peer transactions that anyone could verify.
Today, thousands of cryptocurrencies exist, each with different purposes. Some are built for payments, others power smart contracts, decentralized apps (dApps), or even digital collectibles.
In short, cryptocurrency is more than just digital money.
It’s a new financial infrastructure, global, borderless, transparent, and open to anyone with an internet connection.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
To understand how cryptocurrency works, you need to know three key pillars:
blockchain technology, cryptographic security, and decentralized peer-to-peer networks.
Together, they make crypto secure, transparent, and nearly impossible to manipulate.
Blockchain Technology Explained
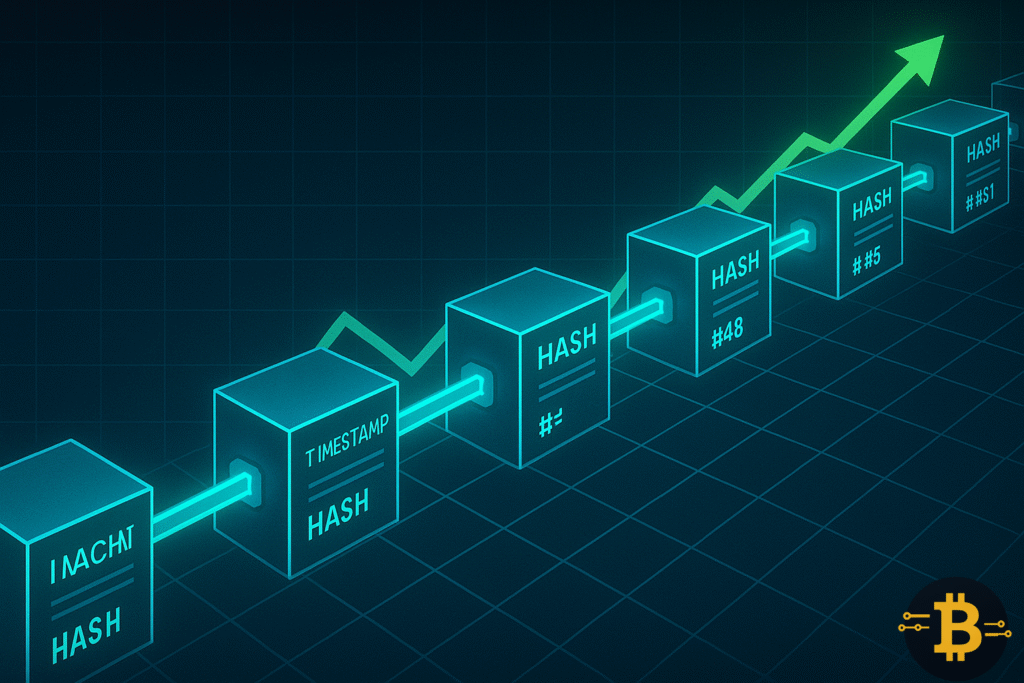
At the heart of every cryptocurrency lies the blockchain, a digital ledger that records all transactions made on the network.
Instead of being stored in one central place, this ledger is distributed across thousands of computers (called nodes). Each node keeps a copy of the entire transaction history.
When new transactions occur, they’re grouped into “blocks.”
Each block includes transaction details, a timestamp, and a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block. This creates a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
Because every block depends on the one before it, tampering with past data is practically impossible. If someone tried to alter one block, it would break the chain and be instantly rejected by the rest of the network.
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin and several other blockchains.
Here’s how it works:
- Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles using powerful computers.
- The first miner to solve the puzzle adds the next block to the chain.
- That miner receives a reward in newly minted cryptocurrency.
This process secures the network by making attacks extremely costly.
As of 2025, the Bitcoin network’s hash rate, a measure of computing power, exceeds 400 exahashes per second, making it one of the most secure systems on Earth.
However, PoW consumes a lot of energy, which is why newer blockchains have turned to an alternative.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake replaces energy-intensive mining with staking.
Instead of running massive machines, validators lock up (or “stake”) a certain amount of their cryptocurrency to help confirm transactions.
- Validators are chosen randomly, based on the amount they’ve staked.
- Honest behavior is rewarded with transaction fees.
- Dishonest actions are punished by losing part of the stake, a process called slashing.
Ethereum, the second-largest blockchain, transitioned to Proof of Stake in 2022 during an event called The Merge.
This change reduced its energy use by over 99.95%, while still maintaining strong network security.
To run a validator node on Ethereum today, you need to stake at least 32 ETH.
Cryptographic Security
Cryptocurrency security is built on public-key cryptography.
Each user has two keys:
- A public key, which acts like your crypto “address.”
- A private key, which proves ownership and allows you to send funds.
Transactions are digitally signed with private keys, making them verifiable but impossible to forge.
Most modern blockchains use the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) a proven encryption standard.
And as computing power advances, developers are exploring quantum-resistant algorithms to prepare for the next generation of threats.
Decentralization and Peer-to-Peer Networks
Unlike banks or payment processors, cryptocurrencies run on peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. That means there’s no central server or authority. Every node on the network helps validate transactions, keeping the system alive and secure even if parts of it go offline.
This decentralized structure prevents censorship and reduces single points of failure.
Even if one region or server goes down, the network continues operating globally 24/7, without permission from anyone.
Consensus algorithms (like PoW and PoS) ensure that all nodes agree on which transactions are valid.
This agreement, called Byzantine Fault Tolerance, allows the system to function securely even if some participants act maliciously.
In short:
Cryptocurrencies work because thousands of independent computers agree on one version of the truth, the blockchain.
No one controls it, everyone can verify it, and the code enforces the rules automatically.
Why Crypto Investing Matters in 2025
The year 2025 marks a turning point for cryptocurrency.
What was once a speculative digital asset has evolved into a recognized investment class, attracting both retail investors and global financial giants.
Let’s look at why this moment matters and why understanding crypto now could shape your financial future.
1. Institutional Adoption Has Gone Mainstream
For years, crypto struggled to earn legitimacy. That changed dramatically in 2024, when the U.S. approved Bitcoin Spot ETFs.
This milestone opened the door for institutional investors, including BlackRock, Fidelity, and JPMorgan, to directly offer crypto exposure to clients.
Within the first six months, Bitcoin ETFs attracted over $15 billion in inflows, pushing Bitcoin’s market capitalization back above $1.3 trillion.
Crypto is no longer a niche playground; it’s part of the global financial system.
2. Central Banks Are Building Their Own Digital Currencies
Governments aren’t ignoring this trend either.
More than 130 countries are now developing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) government-backed tokens that operate on blockchain technology.
CBDCs show that crypto’s core idea, digital, borderless, programmable money, has influenced even the most traditional institutions.
They also signal an ongoing convergence between crypto and traditional finance (TradFi), paving the way for smoother global payments and faster cross-border transfers.
3. DeFi and Web3 Are Reshaping How We Use Money
The decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem now holds over $90 billion in total value locked (TVL).
This includes lending protocols, decentralized exchanges, and staking platforms where users earn rewards by participating directly, no banks, no middlemen.
Meanwhile, Web3 platforms are turning digital ownership into reality through NFTs, DAOs, and metaverse economies.
These innovations are not just speculative; they’re functional, driving new business models that reward users instead of corporations.
4. Crypto as a Hedge and Lifeline
In countries facing inflation, currency devaluation, or unstable banking systems, crypto has become a financial lifeline.
Emerging markets across Africa, Asia, and Latin America are adopting stablecoins for remittances and cross-border payments.
Because many cryptocurrencies have fixed supplies (like Bitcoin’s 21 million limit), they serve as a hedge against inflation similar to gold, but more portable and accessible.
5. The Convergence of Regulation and Innovation
The crypto market is maturing. Governments worldwide are developing clearer regulations, exchanges are improving security and compliance, and investors have more protection than ever before.
This blend of trust + transparency is what’s fueling the next wave of adoption.
2025 isn’t just another bull cycle; it’s the start of a financial shift.
Crypto is evolving from an alternative to an essential. And whether you’re an investor, trader, or builder, understanding this transformation now puts you ahead of the curve.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
Not all cryptocurrencies serve the same purpose. Some act as digital money, others power smart contracts, and a few even represent ownership of real-world assets.
Understanding the different types of cryptocurrencies helps you know what you’re investing in and why each category exists.
1. Payment Cryptocurrencies
These are the original purposes of crypto: digital cash for global payments.
They’re built for fast, low-cost transactions without banks or middlemen.
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and largest cryptocurrency, often called “digital gold.” Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, making it scarce and deflationary. It’s trusted as a long-term store of value and is now used by institutions through ETFs and corporate treasuries.
- Litecoin (LTC): A “lighter” version of Bitcoin with faster transactions (2.5-minute blocks vs Bitcoin’s 10). It’s often used for small payments and testing new blockchain features.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Created from a Bitcoin fork to increase transaction speed and lower costs. It focuses on being usable for everyday purchases.
- Monero (XMR): A privacy-focused coin that hides transaction details. Monero is popular with users who value anonymity and untraceable transfers.
2. Utility Tokens
Utility tokens give users access to specific products or services within a blockchain ecosystem. They don’t represent ownership; instead, they power operations on their respective networks.
- Ethereum (ETH): The foundation of decentralized apps (dApps) and smart contracts. ETH is used to pay for “gas fees”, transaction costs when executing smart contracts.
It’s the backbone of most Web3 applications. - Chainlink (LINK): A decentralized oracle network that connects blockchains to real-world data, such as price feeds or weather data. LINK makes DeFi apps functional and trustworthy.
- Basic Attention Token (BAT): Used in the Brave Browser, it rewards users for viewing ads and helps advertisers reach genuine audiences.
- Filecoin (FIL): Powers a decentralized cloud storage network, letting users rent out unused data space securely.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are designed to keep a steady value, usually pegged to the U.S. dollar or another asset. They’re the bridge between traditional finance and crypto, easy to trade, spend, or hold during volatile markets.
- Tether (USDT): The largest stablecoin by market cap (over $120 billion). Widely used on exchanges for liquidity and fast settlements.
- USD Coin (USDC): Managed by Circle and regularly audited for transparency. Known for its regulatory compliance and popularity among institutions.
- Dai (DAI): A decentralized stablecoin backed by crypto collateral (mainly ETH). Managed by the MakerDAO community, not a company.
- Tether Gold (XAUT): Pegged to the price of physical gold, offering stability backed by a real-world asset.
4. Security Tokens
Security tokens represent ownership rights in real-world assets like real estate, stocks, or bonds. They’re subject to securities laws and are often used in regulated investment platforms.
- tZERO and Polymath are examples of projects that tokenize traditional assets for blockchain-based trading.
Holders may receive dividends, interest, or profit shares — similar to owning stock, but on-chain.
5. Governance Tokens
These tokens allow holders to vote on decisions that affect the future of a blockchain protocol.
Think of them as digital voting shares for decentralized organizations.
- Uniswap (UNI): Used to vote on upgrades to the Uniswap decentralized exchange.
- Aave (AAVE): Holders can influence how lending rates and risk parameters are set.
- Compound (COMP): Powers governance in a major DeFi lending platform, giving users control over protocol improvements.
Owning these tokens means you have a voice in how projects evolve, one of the core principles of decentralization.
6. Memecoins
Memecoins are born from internet culture and community hype.
They often start as jokes but can gain huge followings and trading volumes.
- Dogecoin (DOGE): Originally a meme, DOGE became popular for its active community and celebrity endorsements. It’s even used for micro-tipping online.
- Shiba Inu (SHIB): Inspired by Dogecoin but built on Ethereum. SHIB has evolved into a full ecosystem with DeFi and NFT elements.
- Pepe (PEPE): A newer memecoin representing meme culture in crypto. Extremely volatile, more driven by sentiment than fundamentals.
Important: Memecoins are high-risk and largely speculative.
Invest only what you can afford to lose.
7. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs represent unique digital assets such as art, collectibles, or gaming items.
Each NFT is one-of-a-kind and verified on the blockchain; you can’t swap one for another like you can with Bitcoin.
- Built mainly on Ethereum (ERC-721 / ERC-1155 standards).
- Used in gaming, digital art, domain names, and metaverse assets.
- The NFT market reached $25 billion in trading volume by 2024.
NFTs gave creators new ways to monetize their work and helped drive mainstream awareness of blockchain technology.
8. Platform Cryptocurrencies
Platform tokens power the blockchains that host other projects and apps.
They form the infrastructure layer of the crypto world.
- Ethereum (ETH): Still the largest smart contract platform with thousands of projects built on it.
- Solana (SOL): Known for high transaction speed (up to 65,000 TPS) and low fees, a favorite among DeFi and NFT developers.
- Polkadot (DOT): Enables different blockchains to connect and share data through “parachains,” enhancing interoperability.
- Cardano (ADA): Focused on scientific research and sustainable blockchain design. Popular in developing countries for identity and education solutions.
Final Thoughts on Crypto Categories
Each type of cryptocurrency serves a unique purpose.
Understanding these categories helps you build a balanced portfolio mixing utility, stability, and long-term growth potential.
The key is to know what each coin is meant to do before you invest.
Next, let’s prepare you for the most important step: buying your first crypto safely.
How to Prepare Before Buying Crypto
Before you buy your first cryptocurrency, you need to understand one thing: this market rewards preparation as much as opportunity.
Crypto moves fast, trades 24/7, and can swing 10–30% in a single day. The difference between profit and panic often comes down to education and planning.
Here’s how to prepare wisely before investing.
Financial Literacy: The Crypto Edition
Start by understanding the basics of how crypto markets work.
Unlike stocks or forex, cryptocurrencies trade around the clock with no centralized exchange. Prices are driven by supply, demand, and sentiment not company earnings or government policies.
Here’s what to study first:
- Market capitalization – shows the total value of a coin.
- Circulating supply – how much is currently available.
- Tokenomics – how tokens are created, distributed, and burned.
- Whitepapers – project roadmaps that explain real-world utility.
Also, learn to read simple price charts and candlestick patterns.
This helps you understand momentum, identify support/resistance levels, and make smarter entries.
Finally, always follow credible news sources and official project updates. Avoid chasing social media hype; it’s one of the easiest ways to lose money fast.
Know Your Risk Tolerance
Crypto investing isn’t one-size-fits-all.
Your risk tolerance depends on your financial goals, income stability, and emotional control during market swings.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Conservative investors: Allocate 1–5% of portfolio to crypto.
- Moderate investors: Around 5–15%.
- Aggressive investors: Up to 30%, but only with strong market knowledge.
No matter your style, never invest money you can’t afford to lose.
If you’re starting small, consider Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) investing a fixed amount at regular intervals. This reduces the impact of volatility and helps you build a position over time.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Even smart investors make rookie errors in crypto.
Here are the most common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Not enabling 2FA: Always protect your accounts with two-factor authentication (Google Authenticator or Authy).
- Keeping funds on exchanges: After buying, move your crypto to a secure wallet.
- Falling for scams: Avoid promises of guaranteed returns or secret “signals.”
- Ignoring taxes: Every trade or sale can be taxable; keep records.
- Letting emotions lead: Fear and greed cause more losses than bad projects do.
Crypto rewards discipline. Treat it like any serious investment study, plan, and execute with patience.
How to Start Investing in Crypto Step by Step

You’ve learned the basics, now it’s time to take action.
Buying crypto is simple once you understand the process, but getting it right the first time saves you from costly mistakes later.
Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough for beginners.
Step 1: Choose a Trusted Crypto Exchange
The first step is picking a reliable exchange where you can buy, sell, and store crypto.
Look for platforms with a strong reputation, security certifications, transparent fees, and responsive customer support.
| Exchange | Fees | KYC Required | Ease of Use | Supported Coins |
| Coinbase | 0.5 – 4.5 % (higher for instant buys) | Yes | Beginner-friendly; simple interface | 280 + |
| Binance | 0.1 % (0.075 % with BNB) | Yes (tiered) | Advanced tools; lower fees | 600 + |
| Bybit | 0.1 % spot / 0.06 % futures | Yes (for withdrawals > $2000 daily) | Intermediate; popular for copy & bot trading | 400 + |
| Kraken | 0.16 – 0.26 % depending on volume | Yes (multiple tiers) | Professional-grade; excellent security | 200 + |
Tip: For your first purchase, start with Coinbase or Binance.
They’re beginner-friendly and widely trusted worldwide.
Step 2: Create and Verify Your Account
- Sign up using your email and create a strong password.
- Complete KYC verification, upload a government-issued ID, and proof of address.
- Add two-factor authentication (2FA) immediately to protect your account.
Verification usually takes a few minutes, but it ensures compliance with security and anti-fraud laws.
Step 3: Deposit Funds
Once verified, you can fund your account using:
- Bank transfer (ACH, SEPA, wire): Lowest fees, takes 1–2 days.
- Debit or credit card: Instant, but higher fees.
- PayPal or digital payments: Convenient, region-dependent.
- Crypto deposits: Transfer from another wallet if you already own some coins.
Always double-check the currency and network type before sending funds; a wrong selection can cause permanent loss.
Step 4: Buy Your First Cryptocurrency
With funds available, you’re ready to buy.
Most beginners start with Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH) because of their stability, liquidity, and strong track record.
- Choose your trading pair (e.g., BTC/USD).
- Enter the amount you want to buy (start small, even $50 to $100).
- Review the transaction and confirm.
Once purchased, move your coins to a personal wallet rather than leaving them on the exchange.
This step gives you full ownership and control over your funds.
Top Cryptocurrencies to Watch in 2025
Here’s the thing: not all cryptos are built the same.
Some lead the entire market. Others are up-and-comers with real potential. And then there are coins that are pure hype (we’ll skip those).
If you’re just getting started, focus on projects that actually do something useful, ones that have solid tech, strong teams, and real adoption.
These are the coins worth keeping on your radar in 2025.
Table: Top Crypto Picks for 2025
| Cryptocurrency | Highlights (Why It Matters) |
| Bitcoin (BTC) | The king of crypto. Bitcoin isn’t just the first, it’s still the most trusted. With over $2.4T market cap and fresh ETF approval, institutions are buying it like digital gold. Add in the 2024 halving (cutting new supply in half), and scarcity is driving serious long-term demand. |
| XRP (Ripple) | After years of legal battles, Ripple finally got clarity from the SEC, and that’s huge. Banks and payment networks are now integrating XRP for fast, low-cost international transfers. It moves money across borders in seconds, not days. |
| Astar (ASTR) | Japan’s leading Web3 project, backed by Sony Network and connected to Polkadot. Astar focuses on enterprise-grade blockchain solutions and developer tools. It’s one of Asia’s most promising growth chains heading into 2025. |
| Avalanche (AVAX) | Built for speed — up to 4,500 transactions per second — and low fees. Avalanche’s subnet technology lets businesses create their own custom blockchains. With AWS partnerships and a growing DeFi ecosystem, it’s earning major respect. |
| Cardano (ADA) | Known for its research-driven approach. Every upgrade is peer-reviewed before launch. Cardano is pushing adoption in Africa through digital ID and education projects. Combine that with energy efficiency and smart contracts, and ADA remains a long-term sleeper favorite. |
Why These Coins Stand Out
If you notice something, every coin on that list has one thing in common: real-world use cases.
Bitcoin protects value. XRP moves money. Astar builds infrastructure. Avalanche scales the system. Cardano connects crypto to real communities.
That’s what you want to look for as an investor, not hype, but utility.
Another point: these coins are also listed on major exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Bybit, which makes them easy to access and liquid (meaning you can buy or sell anytime without crazy slippage).
Investing vs Trading
When you enter the crypto market, it’s important to understand the difference between investing and trading.
Both can be profitable, but they require completely different mindsets, skills, and time commitments.
Investing: The Long-Term Approach
Investing in cryptocurrency means buying and holding digital assets for an extended period, usually months or years. The goal is to benefit from long-term price appreciation driven by adoption, innovation, and network growth.
Key Characteristics:
- Focuses on fundamentals such as project utility, developer activity, and long-term vision.
- Requires patience rather than constant monitoring.
- Often involves strategies like staking or yield farming to earn passive income.
- Suitable for people who want exposure to the market without daily trading stress.
Example:
A Bitcoin investor who bought in 2016 and held through market cycles has seen over 10x growth, despite multiple 70% corrections.
Long-term investing also benefits from lower tax rates in many countries, as gains held for more than a year may qualify for capital gains treatment instead of ordinary income tax.
Trading: The Active Strategy
Trading, on the other hand, involves frequent buying and selling to profit from short-term price movements.
Traders use technical analysis (TA), chart patterns, and market indicators to predict direction and timing.
Key Characteristics:
- Focuses on price action and short-term volatility.
- Requires deep understanding of tools like support/resistance, moving averages, and volume analysis.
- Time-intensive, success depends on constant market monitoring.
- Involves higher risk due to leverage, fees, and human emotion.
While trading offers higher potential returns, studies show that only 10 to 15% of traders remain consistently profitable over time.
The rest often lose due to poor risk management, emotional decisions, or a lack of a proven system.
Core Differences
| Aspect | Investing (HODL) | Trading |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (1+ years) | Short to mid-term (minutes to months) |
| Focus | Fundamentals, adoption | Price action, volatility |
| Risk Level | Moderate to low | High |
| Tax Treatment | Long-term capital gains | Short-term income rates |
| Effort Required | Minimal | High |
| Emotional Pressure | Low | High |
Choosing the Right Path
If you’re just starting out, it’s generally better to begin as an investor, not a trader.
Long-term investing allows you to learn the market, develop confidence, and avoid costly mistakes.
Once you’ve mastered the basics and understand technical analysis, you can gradually test trading with small capital and strict risk controls.
Whether you invest or trade, always define your goals, risk tolerance, and exit strategy before entering any position.
How to Store Your Crypto Safely
Owning cryptocurrency comes with a powerful responsibility; you are your own bank.
That means you control your money directly, but you’re also fully responsible for keeping it secure.
Unlike traditional accounts, there’s no password reset or customer support if you lose your crypto keys.
Understanding how to store your cryptocurrency safely is essential for protecting your investment long-term. Let’s go through the main storage options, best practices, and security measures step by step.
Wallet Storage Options
Cryptocurrencies are stored in digital wallets, which hold your public and private keys.
There are several types, each offering different levels of convenience and security.
1. Hardware Wallets (Cold Storage)
Hardware wallets are physical devices that store your private keys offline.
They’re considered the safest option for long-term holding because they’re immune to online hacks.
Popular Examples:
- Ledger Nano X: Supports over 5,500 coins, Bluetooth connectivity, and a mobile app.
- Trezor Model T: Features a touchscreen, open-source firmware, and strong community trust.
- Coldcard: A Bitcoin-only wallet designed for maximum security and air-gapped transactions.
Advantages:
- Completely offline (no exposure to malware).
- Protected by PIN codes and recovery phrases.
- Ideal for storing large amounts of crypto.
Disadvantages:
- Costs between $100–$250.
- Slightly less convenient for daily transactions.
If you plan to hold your crypto for the long term, a hardware wallet is non-negotiable.
2. Software Wallets (Hot Wallets)
Software wallets are apps installed on your phone, computer, or browser.
They’re convenient and free, but because they’re connected to the internet, they carry higher security risks.
Popular Options:
- Mobile wallets: Trust Wallet, MetaMask Mobile, Exodus.
- Desktop wallets: Electrum, Atomic Wallet, Exodus Desktop.
- Browser wallets: MetaMask Extension, MyEtherWallet.
Advantages:
- Free and easy to set up.
- Accessible for frequent transactions or DeFi activity.
Disadvantages:
- Vulnerable to hacking, malware, and phishing.
- Not suitable for storing large holdings long-term.
Best Practice:
Use hot wallets only for spending or trading amounts, and move the rest to cold storage.
3. Paper Wallets
Paper wallets are physical printouts of your public and private keys.
They were once a popular cold storage method but are now mostly outdated.
Advantages:
- Fully offline and immune to cyberattacks.
- Simple to create and store.
Disadvantages:
- It can be damaged by water, fire, or fading ink.
- Difficult to use for spending or transferring funds.
- No protection against physical theft.
Modern hardware wallets now make paper wallets largely unnecessary, but they can still work as backup storage if handled carefully.
Seed Phrase Security
When you create a wallet, you’ll be given a seed phrase, usually 12 or 24 random words.
This phrase is the master key to your funds. Anyone with access to it can control your crypto.
Security Rules:
- Never store your seed phrase digitally (no screenshots, emails, or cloud storage).
- Write it down on paper or engrave it on a metal backup plate (e.g., Cryptosteel).
- Store it securely in multiple physical locations.
- Never share it with anyone; no legitimate service will ever ask for it.
If you lose your seed phrase, your crypto cannot be recovered.
If someone else gets it, your crypto can be stolen instantly.
Treat it with the same seriousness as your passport or vault key.
Authentication and Access Control
Even with secure wallets, you still need to protect your accounts and devices.
Here’s how to strengthen your setup:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Use apps like Google Authenticator or Authy, not SMS.
- Whitelist withdrawal addresses: Allow transfers only to pre-approved wallets.
- Set up withdrawal limits and email confirmations for added safety.
- Use unique, complex passwords, 20+ characters with symbols and numbers.
- Consider password managers like 1Password or Bitwarden to store credentials securely.
- Activate biometric login (fingerprint or face ID) if your device supports it.
Avoiding Common Threats
Cyber threats in crypto are real, but most are preventable.
Here are the most common ones to watch out for:
- Phishing: Fake websites or emails pretending to be exchanges. Always check URLs carefully.
- Malware: Avoid downloading unverified software or clicking unknown links.
- SIM Swapping: Attackers hijack your phone number to bypass 2FA. Use authenticator apps instead.
- Fake Wallets or Extensions: Download only from official websites or verified app stores.
- Clipboard Hijacking: Double-check addresses before confirming a transaction.
- Public Wi-Fi Risks: Never log into wallets or exchanges on open networks. Use a VPN.
Staying alert can eliminate 90% of all security risks.
Portfolio Management Strategy
Protecting your crypto isn’t just about security it’s also about managing your holdings efficiently.
Best Practices:
- Keep 80–90% of your portfolio in cold storage (hardware wallets).
- Reserve 10–20% in hot wallets for trading or daily use.
- Rebalance your holdings quarterly or semi-annually to maintain risk targets.
- Take partial profits during strong rallies to secure gains.
- Conduct a security checkup every few months, update passwords, verify recovery options, and test wallet backups.
Think of your crypto like a business: your assets, your responsibility.
In summary:
Safe storage isn’t optional; it’s the foundation of every successful crypto investor’s strategy.
Your goal is simple: accessibility for daily use, protection for long-term wealth.
Legal & Tax Essentials
Cryptocurrency isn’t just about trading and technology; it also carries legal and tax responsibilities.
As global adoption grows, governments are introducing new frameworks to regulate, tax, and monitor digital assets.
Understanding these rules early helps you stay compliant, avoid penalties, and manage your portfolio professionally.
This section covers everything you need to know about crypto taxes, reporting requirements, and the laws shaping this evolving space.
Understanding Crypto Tax Basics
In most countries, cryptocurrency is treated as property, not currency.
That means every time you sell, trade, or use crypto to pay for goods or services, it creates a taxable event.
The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS), for example, classifies crypto under capital assets, the same category as stocks or real estate.
Key Points:
- Capital gains tax applies when crypto appreciates in value before you sell it.
- Ordinary income tax applies to crypto earned from staking, mining, or airdrops.
- The amount you owe depends on how long you held the asset:
- Short-term (under 1 year): Taxed at your regular income rate (10–37%).
- Long-term (1+ years): Lower capital gains rates (0%, 15%, or 20%).
- Short-term (under 1 year): Taxed at your regular income rate (10–37%).
Proper record-keeping is crucial because exchanges are now required to report transactions directly to tax authorities.
Common Taxable Events
These are the main situations where you’ll owe taxes on crypto:
- Selling crypto for fiat (USD, EUR, NGN, etc.)
- Trading one cryptocurrency for another (e.g., BTC → ETH)
- Spending crypto on goods or services
- Receiving crypto as payment for freelance work or salary
- Earning staking or mining rewards
- Receiving airdrops or forked tokens
Each of these must be recorded with the date, amount, fair market value, and cost basis (the original purchase price).
Non-Taxable Activities
Not every crypto transaction is taxable. The following are generally exempt:
- Buying crypto with fiat and holding it.
- Transferring assets between your own wallets.
- Gifting crypto within the annual tax-free limit (up to $18,000 in 2025, U.S. standard).
- Donating crypto to registered charities.
- Inheriting crypto (with a stepped-up cost basis applied).
Understanding the difference between taxable and non-taxable actions helps you minimize tax liability legally.
Tax Reporting Requirements
If you file taxes in jurisdictions like the United States, Canada, the UK, or the EU, you’ll likely encounter crypto-related forms.
In the U.S., these include:
- Form 8949: Reports capital gains and losses.
- Schedule D: Summarizes total capital gains from all investments.
- Schedule 1: Declares additional income from mining, staking, or airdrops.
- Form 1040: The main tax return, which now includes a direct question about crypto ownership.
- FBAR (FinCEN 114): Required if you hold more than $10,000 in foreign exchanges.
- FATCA (Form 8938): For reporting offshore crypto assets.
Failure to report crypto taxes can result in severe penalties up to 75% of the unpaid tax, plus interest and potential criminal charges.
Pro Tip: Use dedicated crypto tax software such as Koinly, CoinTracker, or CryptoTrader.Tax to automatically calculate gains and generate reports.
Record-Keeping Essentials
Accurate records are the foundation of tax compliance.
You should maintain detailed documentation for every crypto transaction.
Information to Record:
- Date and time of each transaction
- Type of transaction (buy, sell, swap, earn, transfer)
- Amount and fair market value in your local currency
- Wallet addresses or exchange accounts involved
- Gas fees or transaction costs (deductible as expenses)
Keep records for at least seven years to stay audit-ready.
Deducting Crypto Losses
Crypto markets are volatile, and not every trade results in profit. The good news is — losses can help offset your tax bill.
Here’s how it works:
- Capital losses offset capital gains in the same year.
- If your losses exceed gains, you can deduct up to $3,000 against regular income annually.
- Any remaining losses can be carried forward to future tax years.
- The wash sale rule (which prevents claiming losses if you re-buy an asset too quickly) currently doesn’t apply to crypto — though this could change with new regulations.
Strategic loss harvesting can turn a bad trade into a useful tax advantage.
Legal Compliance Requirements
As regulation tightens, exchanges and crypto businesses are required to follow KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws.
Key Compliance Areas:
- Verified identity before trading or withdrawals.
- Travel Rule: Transactions above $3,000 must include sender and receiver information.
- Licensing: Exchanges must register with financial authorities in their jurisdiction.
- Security Tokens: Must comply with securities laws similar to company shares.
These regulations aim to protect users, prevent fraud, and build trust in the crypto industry.
How Tax Authorities Track Crypto
Many investors assume crypto is anonymous, but it’s not.
Blockchain transactions are public, and specialized firms like Chainalysis, Elliptic, and CipherTrace help governments analyze on-chain data.
Authorities can trace wallet activity, identify exchange accounts, and link transactions to individuals through KYC records.
Major exchanges now issue Form 1099 reports to the IRS and share information with other tax agencies globally.
Crypto anonymity is a myth; transparency is built into the system.
International Considerations
Crypto laws and taxes vary widely by country.
Here’s a brief overview:
- United States, Canada, EU, Japan, Australia: Legal, regulated, and taxable.
- Portugal & Germany: Offer crypto-friendly policies, often exempting long-term holdings.
- India: Allows trading but imposes 30% tax on profits.
- China: Bans crypto trading completely.
- Nigeria: Legal but under close regulatory observation by the Central Bank and SEC.
If you hold assets across multiple countries, consult a tax professional familiar with multi-jurisdictional crypto law to avoid double taxation or reporting errors.
In summary:
Crypto taxation is becoming more structured each year.
Keeping detailed records, understanding your obligations, and staying compliant will protect your portfolio and peace of mind.
Remember, profits are only real when they’re legal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Even after reading a complete guide, it’s natural to still have a few questions. Here are the most common ones beginners ask when learning about cryptocurrency, answered in simple, straightforward terms.
1. Is cryptocurrency legal?
Yes, cryptocurrency is legal in most countries, including the United States, Canada, the European Union, Japan, Australia, and Nigeria.
However, regulations differ by jurisdiction. Some countries, like China, have banned trading and mining completely. Others, such as Portugal and Germany, have implemented crypto-friendly tax policies.
Always check your local laws before buying or trading.
2. How much money do I need to start trading crypto?
You can start with as little as $10 to $50 on most exchanges.
However, a $100–$500 starting amount is often recommended for meaningful learning and portfolio tracking.
Because crypto supports fractional ownership, you can buy small portions of expensive coins like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
3. Can I lose all my money in cryptocurrency?
Yes, it’s possible.
Crypto assets are volatile, and prices can drop 20–50% in days. Projects can fail, exchanges can be hacked, or private keys can be lost.
To reduce risk:
- Only invest money you can afford to lose.
- Diversify across several reputable coins.
- Store your funds securely using hardware wallets.
Responsible investing and risk management make total loss unlikely, but the possibility always exists.
4. What’s the difference between a hot wallet and a cold wallet?
- Hot wallets are connected to the internet (mobile or web wallets). They’re convenient for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to hacks.
- Cold wallets stay offline (hardware or paper wallets). They’re ideal for long-term storage and significantly more secure.
A common strategy is to keep small amounts in hot wallets for trading and large holdings in cold storage.
5. How do I cash out my cryptocurrency?
You can sell crypto directly on an exchange and withdraw to your bank account.
Other options include:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms that match buyers and sellers.
- Crypto ATMs, though they often have higher fees.
- Payment processors like BitPay convert crypto to fiat for merchants.
Withdrawal times usually take 1–5 business days, depending on your payment method and region.
6. Are crypto earnings taxable?
Yes.
Earnings from trading, selling, staking, mining, or receiving crypto payments are taxable income in most countries.
You’ll owe capital gains tax if your crypto increased in value since purchase, and ordinary income tax for staking rewards or airdrops.
Always maintain detailed records and consult a tax professional for your jurisdiction.
7. What are gas fees, and why do they exist?
Gas fees are transaction costs paid to miners or validators for processing and securing transactions on a blockchain.
They compensate the network for computational power and prevent spam attacks.
Gas fees vary based on network congestion — for example, Ethereum gas can range from $1 to $50 depending on activity.
8. How can I earn free crypto as a beginner?
You can earn small amounts of crypto through:
- Exchange bonuses (sign-up rewards, referral programs).
- Learning platforms like Coinbase Earn or Binance Learn & Earn.
- Staking rewards from proof-of-stake tokens.
- Airdrops are distributed by new projects.
- Play-to-earn games and blockchain loyalty programs.
Be cautious of scams that promise unrealistic returns — always verify the source.
9. What’s the best cryptocurrency for beginners to buy?
For beginners, it’s best to start with established, reputable coins that have strong track records and liquidity.
Recommended options include:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The most stable and widely recognized.
- Ethereum (ETH): Powers smart contracts and most Web3 projects.
- Solana (SOL): Known for speed and low fees.
Avoid speculative memecoins or new tokens until you gain experience.
10. How long does it take to become profitable in crypto trading?
It depends on your strategy and discipline.
Most beginners take 6–12 months just to understand market behavior and manage emotions.
Consistent profitability often comes after 2–3 years of learning, practicing, and refining a proven trading system.
Patience, education, and risk control are the real keys to success, not luck.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency is reshaping the global economy.
It’s opening access to financial systems, empowering individuals, and creating opportunities for those willing to learn.
But it’s also a space that rewards preparation and awareness.
By understanding how crypto works, managing risk, securing your assets, and staying compliant with regulations, you’re already ahead of most beginners.
The technology is still evolving, and so is the opportunity.
Start small, stay consistent, and focus on learning before earning.

