In 2023, crypto scams cost victims over $5.6 billion globally – a 45% increase from the previous year.
If you’re reading this, you’re either worried about becoming a victim or want to protect your crypto assets. The good news? Learning how to avoid crypto scams is simpler than you think.
Crypto scams thrive because blockchain transactions are irreversible, attackers operate anonymously across borders, and many users are still learning the technology. Unlike traditional banking where you can dispute charges or freeze accounts, sending crypto to a scammer means it’s gone forever. This permanence makes prevention your only defense.
After a decade of teaching cryptocurrency security to thousands of beginners and experienced users, I’ve seen every type of scam – and more importantly, I’ve taught people how to spot and avoid them. This guide covers 15 major red flags, explains how cryptocurrency scams actually work, and gives you practical steps to protect your assets. Security isn’t complicated; it’s a habit you can learn today.
Table of Contents
- Common Types of Crypto Scams You Need to Know
- How Crypto Scammers Actually Work (The Psychology)
- 15 Red Flags: Signs You're Looking at a Crypto Scam
- How to Protect Your Crypto Wallet: Essential Security Practices
- Secure Communication: Don't Trust DMs
- On-Chain Security: Understanding What You're Signing
- How to Choose Safe Crypto Platforms and Exchanges
- What to Do If You've Been Scammed (Immediate Action Steps)
- Frequently Asked Questions About Crypto Scams
- Your Crypto Security Checklist: Stay Safe Daily
- Final Thoughts: Security is a Learnable Skill
- About This Guide
- Reference
Common Types of Crypto Scams You Need to Know
This is an article that I’m going to be posting very soon. I know you did not write it, but I’ll need your help with picking out links that I can actually use for
Understanding the types of crypto scams is your first line of defense. Scammers constantly evolve their tactics, but these eight categories cover over 90% of cryptocurrency scams targeting users today. Let’s break down each one with real examples.
Phishing Scams: Fake Websites and Wallet Apps
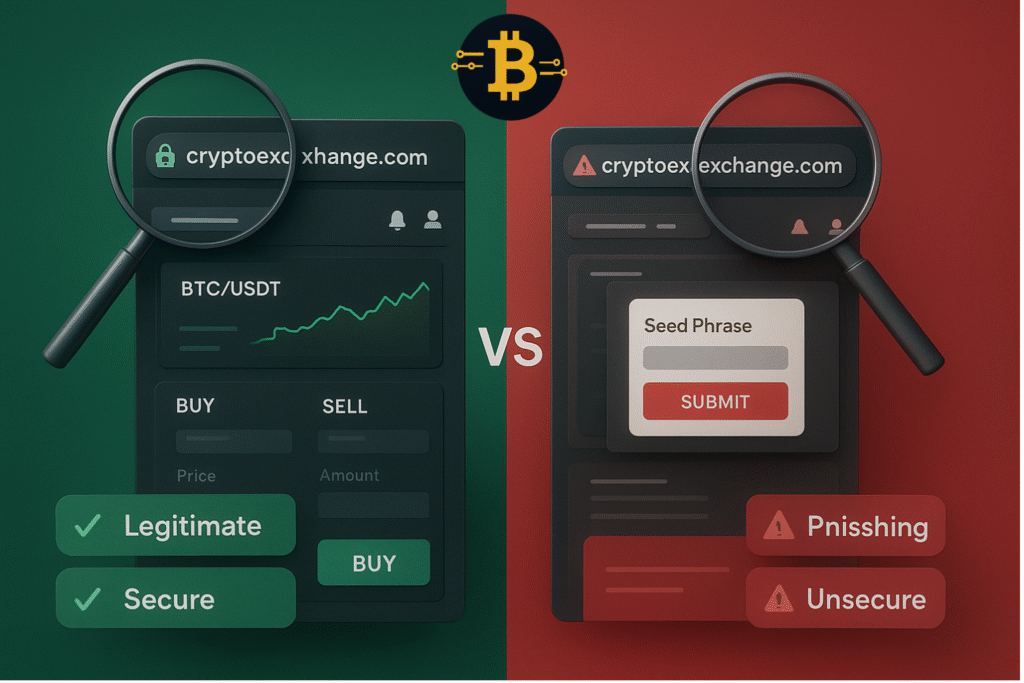
Crypto phishing scams trick users into revealing their private keys or seed phrases by impersonating legitimate services. Scammers create fake versions of popular wallets like MetaMask, exchanges like Coinbase, or DeFi platforms like Uniswap that look identical to the real thing.
How it works: You search for “MetaMask wallet” and click what looks like the official download link – but it’s actually a malicious ad or fake site ranking in search results. You download the fake app, enter your seed phrase to “restore” your wallet, and the scammer instantly drains your funds.
Real example: In 2023, a fake MetaMask app stayed in the Apple App Store for weeks, stealing from hundreds of users before removal. The app had thousands of downloads because it looked professionally designed with fake positive reviews.
The danger lies in the details. These fake sites often use URLs that are incredibly similar to legitimate ones – changing a single letter or adding an extra word. They invest in professional design, copy official branding, and even create fake customer support teams. As a result, even experienced users can fall victim if they’re not paying careful attention.
Investment Scams: Ponzi Schemes and Guaranteed Returns
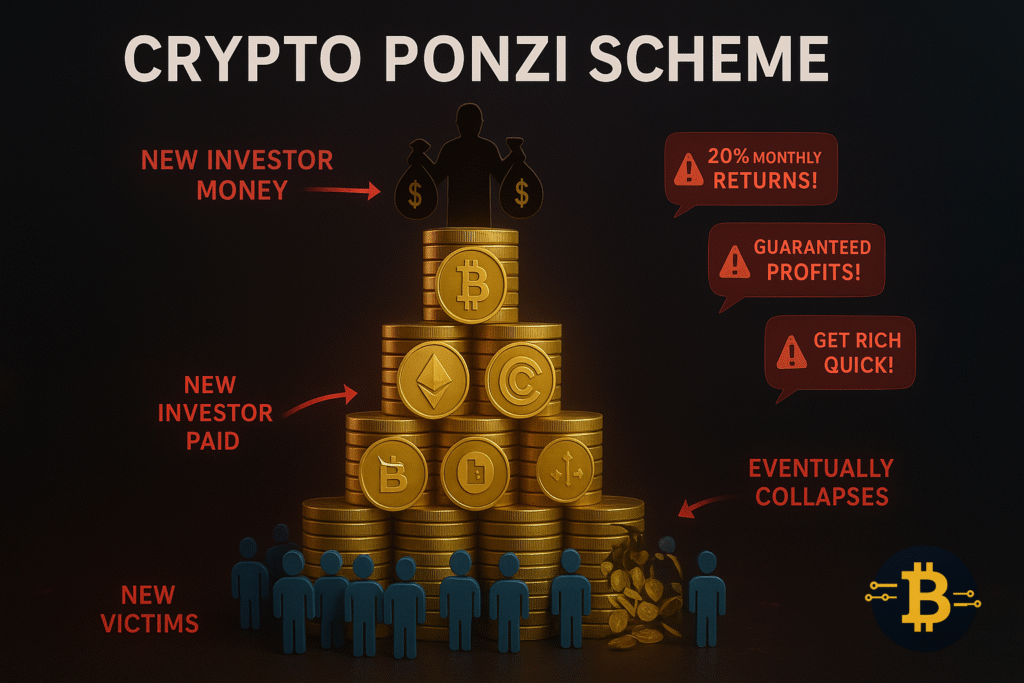
If someone promises to double your crypto or guarantees 20%+ monthly returns, you’re looking at a crypto investment scam. These are digital versions of classic Ponzi schemes, where early investors are paid with money from new investors until the whole thing collapses.
How it works: Scammers create slick websites with fake trading bots, “AI-powered” investment platforms, or “exclusive” staking pools. They show fake profit dashboards, testimonials from “successful investors” (often stolen photos), and urgent pressure to invest before “spots fill up.”
Real example: PlusToken, one of the largest cryptocurrency Ponzi schemes, stole over $2 billion from 3 million victims by promising 9-18% monthly returns. It ran for two years before authorities shut it down – but most victims never recovered their funds.
The psychology behind these scams is powerful. Scammers often show you “proof” of others making money, creating FOMO (fear of missing out). They may even allow you to withdraw small amounts initially to build trust. However, when you invest a larger sum or try to withdraw significant profits, the platform suddenly has “technical issues” or disappears entirely.
Fake Airdrops and Giveaway Scams
Crypto airdrop scams exploit the legitimate practice of projects distributing free tokens. Scammers impersonate real projects or invent fake ones, then ask users to “connect their wallet” or send a small amount of crypto to “verify eligibility” for the airdrop.
How it works: You see a tweet (often from a hacked account or fake profile) announcing a “10,000 ETH giveaway by Vitalik Buterin.” The instructions say to send 0.5 ETH to a wallet address and you’ll receive 5 ETH back. Or worse, you’re asked to connect your wallet to a malicious website that drains everything.
Real example: During the 2021 bull run, fake “Elon Musk giveaway” scams on Twitter stole over $2 million in a single week. Hackers compromised verified accounts to make the scams look legitimate.
Remember this golden rule: Legitimate airdrops never require you to send crypto first. Real projects might ask you to complete social media tasks or hold specific tokens, but they’ll never ask for money upfront.
Romance and Social Engineering Scams
Crypto romance scams use emotional manipulation to exploit victims. Scammers build relationships over weeks or months through dating apps or social media, then eventually introduce a cryptocurrency “opportunity” or request financial help.
How it works: The scammer creates an attractive profile, initiates contact, and invests time building trust through daily conversations. They share fake details about their life, show interest in yours, and gradually bring up their “successful” crypto investments. Eventually, they offer to teach you their strategy or ask for help with a financial situation.
Real statistics: The FBI reported that romance scams cost victims $1.3 billion in 2022, with cryptocurrency increasingly becoming the payment method of choice. Victims lose an average of $15,000 per incident.
These scams are particularly devastating because they combine financial loss with emotional betrayal. The scammer may maintain the relationship for months, making small talk and building genuine-seeming emotional connection. When they finally make their move, victims often ignore red flags because of the perceived relationship.
Impersonation Scams: Fake Customer Support
Impersonation scams involve fraudsters pretending to be customer support representatives, project team members, or community moderators. They reach out via direct message on platforms like Telegram, Discord, or WhatsApp, offering to help with account issues or security concerns.
How it works: You post in a crypto community about a problem you’re having. Within minutes, someone messages you claiming to be from the official support team. They guide you through a “verification process” that involves sharing your seed phrase, connecting your wallet to a fake site, or sending funds for “authentication.”
Critical rule: Real admins, support teams, and project founders never message you first on any platform. If someone claiming to be support contacts you unsolicited, it’s a scam 100% of the time.
I’ve seen countless variations of this scam over the years. Sometimes the scammer’s username is nearly identical to an official account – changing one letter or adding a special character. They often have professional-looking profiles and may even have fake testimonials from other “satisfied users.”
Rug Pulls and Exit Scams
A rug pull occurs when developers launch a cryptocurrency project, build hype to attract investors, then suddenly abandon the project and drain all the funds. This is particularly common with new tokens on decentralized exchanges where anyone can create and list a token in minutes.
How it works: Developers create a token with an exciting name and website, hire influencers to promote it, create artificial hype on social media, and wait for enough investors to buy in. Once the liquidity pool reaches their target amount, they withdraw everything and disappear. The token price crashes to zero.
Real example: Squid Game token (SQUID) surged to $2,856 in November 2021 after riding hype from the Netflix show. Developers then drained $3.38 million from the liquidity pool and vanished. Investors couldn’t sell due to coded restrictions – a deliberate trap.
What is a rug pull in crypto? It’s essentially a sophisticated theft where the creators design the project specifically to steal investor funds. They may spend weeks or even months building credibility, only to pull the rug out when the timing is right.
Malware and Fake Wallet Downloads
Malware-based crypto scams infect your device with software designed to steal your cryptocurrency. This includes clipboard hijackers that change wallet addresses when you paste them, keyloggers that record your passwords and seed phrases, and fake wallet applications that look legitimate.
Common threats:
- Clipboard hijackers: When you copy a wallet address, the malware changes it to the scammer’s address before you paste
- Fake mobile apps: Counterfeit versions of popular wallets in app stores
- Malicious browser extensions: Add-ons that request excessive permissions and steal credentials
- Keyloggers: Record everything you type, including seed phrases
Protection strategy: Only download wallets from official websites (verify the URL carefully), never from search engine ads. Keep your device’s antivirus updated, and be extremely cautious about what browser extensions you install.
Smart Contract Exploits and Blind Signing
Smart contract scams involve malicious code that drains your wallet when you interact with certain decentralized applications. When you “connect your wallet” or “approve” a transaction, you’re often granting permissions without fully understanding what you’re authorizing.
How it works: You discover an exciting new DeFi platform or NFT mint. When you connect your wallet, a popup appears asking for approval. Without reading carefully, you approve “unlimited spending” for the platform. The malicious smart contract can now drain your tokens without additional approval.
Real concern: Many users treat wallet connection as harmless, similar to logging into a website. However, in crypto, these approvals grant actual access to your funds. Unlike a website password, revoking these permissions requires a separate transaction.
The technical nature of smart contracts makes this particularly dangerous. Most users don’t understand Solidity code or what specific permissions mean. Scammers exploit this knowledge gap by making malicious requests look routine.
How Crypto Scammers Actually Work (The Psychology)
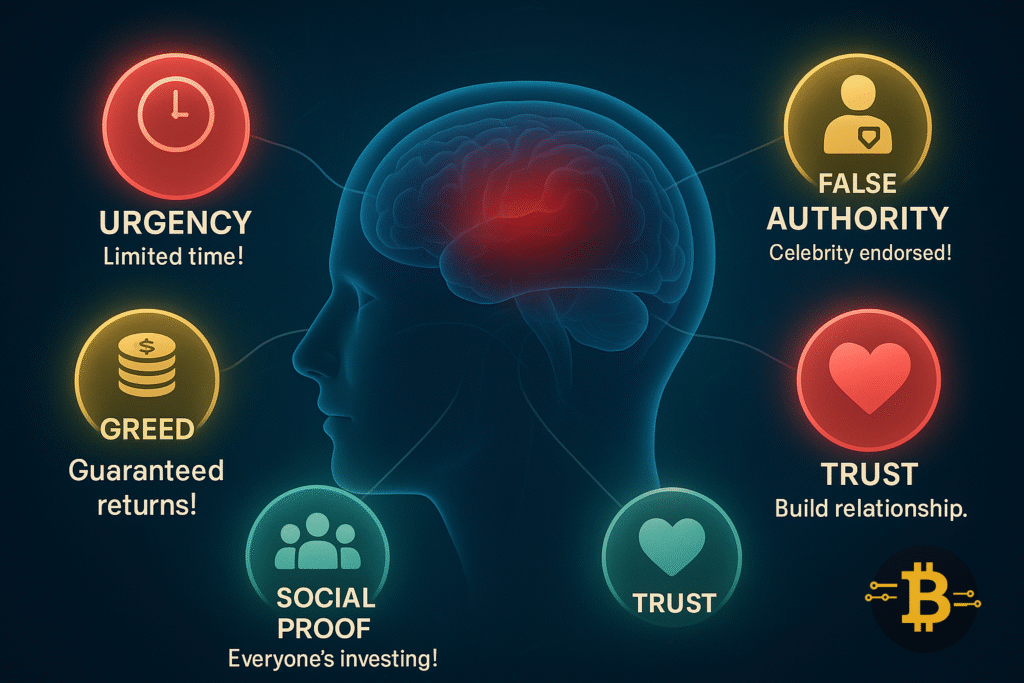
Understanding how crypto scammers work psychologically helps you recognize manipulation tactics before you become a victim. Scammers use proven psychological triggers that bypass logical thinking. Here are the five main tactics:
Tactic 1: Urgency and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
Scammers create artificial urgency: “Only 50 spots left!” or “Offer ends in 2 hours!” This pressure prevents you from doing research or thinking clearly. When you feel rushed, your brain defaults to emotional decision-making rather than logical analysis.
Real opportunities rarely require instant decisions. If someone pressures you to act immediately, that pressure itself is a red flag. Remember: If it’s legitimate today, it’ll be legitimate tomorrow. Take your time to research, ask questions, and verify claims.
Tactic 2: Too-Good-to-Be-True Promises
Guaranteed returns don’t exist in crypto’s volatile market. When someone promises 20% monthly returns or claims to have a “risk-free” investment strategy, they’re lying. These promises exploit greed and the desire for quick wealth.
The mathematical reality is that sustainable investment returns rarely exceed 10-15% annually in traditional markets. Crypto may offer higher potential returns, but they come with proportionally higher risks. Anyone guaranteeing specific returns is either running a scam or has no idea what they’re talking about.
Tactic 3: False Authority and Social Proof
Scammers create fake legitimacy through fabricated endorsements, stolen testimonials, and bot accounts creating artificial hype. They use photos of real people (stolen from LinkedIn or social media) to create fake team profiles. They generate fake audit reports, whitepapers copied from legitimate projects, and fabricated partnership announcements.
Verification is essential: Always check claimed team members on LinkedIn, verify partnerships on the partner’s official website, and confirm audits directly with the audit firm. If you can’t independently verify a claim, assume it’s false.
Tactic 4: Building Trust Then Exploiting It
Some scammers, particularly in romance and long-term investment scams, play the long game. They build trust over weeks or months through consistent communication, small successful transactions, and seemingly genuine relationship-building.
They might start with a small investment opportunity where you actually receive returns. This builds confidence. Then they suggest a larger investment—and that’s when they disappear with your money. This “test the waters” strategy is psychologically powerful because the initial success creates trust.
Tactic 5: Creating Fake Legitimacy
Professional-looking websites, copied branding from legitimate projects, fake team photos, and fabricated partnerships all create an illusion of legitimacy. Scammers understand that visual professionalism influences trust, so they invest in convincing presentation.
This is why you can’t judge a project by its website alone. A professional appearance doesn’t guarantee legitimacy. Instead, verify every claim independently, check social media for real community engagement, and search for independent reviews or warnings.
15 Red Flags: Signs You’re Looking at a Crypto Scam

Here’s a practical checklist of crypto scam red flags. If you see even one or two of these signs, proceed with extreme caution. Three or more? It’s almost certainly a scam.
15 Warning Signs of a Crypto Scam:
- Guaranteed returns or “risk-free” profits – No legitimate investment guarantees returns in crypto’s volatile market. Anyone making this promise is lying.
- Asking for your seed phrase or private keys – No real company, exchange, or support team will EVER request these. This is the crypto equivalent of asking for your bank PIN.
- Pressure to act immediately – Urgency tactics (“offer expires in 1 hour”) prevent due diligence. Legitimate opportunities don’t disappear overnight.
- Unsolicited contact from “support” – Real customer support never messages you first on Telegram, Discord, or social media. This is always a scam.
- Request for “activation fees” or “unlock charges” – You shouldn’t need to pay to withdraw your own money. This is a classic scam tactic to extract more funds.
- Anonymous or fake team members – Legitimate projects have verifiable team members with real LinkedIn profiles and professional histories.
- No smart contract audit – Serious projects get audited by reputable firms like CertiK, Quantstamp, or OpenZeppelin before launch.
- Grammatical errors and poor website quality – Professional projects invest in quality content and design. Multiple spelling errors suggest a rushed scam operation.
- Celebrity endorsements that seem off – Verify on the celebrity’s official channels, not screenshots. Scammers frequently create fake celebrity endorsements.
- Impossible promises (“Double your Bitcoin in 24 hours”) – If it sounds impossible, it is impossible. Don’t let greed override logic.
- No clear explanation of how returns are generated – Legitimate platforms explain their revenue model transparently. Vague answers about “trading algorithms” or “arbitrage” are red flags.
- Pressure to recruit others – This pyramid scheme structure means the project makes money from recruitment, not from any legitimate business activity.
- Wallet approval requests for unlimited spending – Always check what permissions you’re granting. Unlimited approvals let scammers drain your wallet repeatedly.
- Unverified smart contract addresses – Always verify contract addresses on official project websites, never from random links or social media posts.
- No way to contact the team – Legitimate projects have clear communication channels and responsive teams. If you can only reach them through Telegram or anonymous channels, be suspicious.
How to spot a crypto scam? Use this checklist. Even one red flag deserves investigation. Multiple red flags mean you should walk away immediately.
How to Protect Your Crypto Wallet: Essential Security Practices

Your crypto wallet is your bank account, safe, and identity rolled into one. Protecting it requires understanding what makes it vulnerable and implementing proven security practices. Here’s how to protect your crypto wallet properly.
Never Share Your Seed Phrase (Ever)
Your seed phrase is the master key to your crypto. Anyone with access to these 12-24 words can recreate your wallet on any device and steal everything. Here’s the non-negotiable rule:
Never share your seed phrase with anyone. Ever. For any reason.
Not with:
- Customer support (they’ll never ask)
- “Wallet validators” (not a real thing)
- Friends or family (unless you’re creating an inheritance plan)
- Screenshots or text messages (easily hacked)
- Cloud storage (iCloud, Google Drive, Dropbox)
The only person who should know your seed phrase is you. If someone asks for it – even if they seem helpful – they’re trying to scam you. This rule has no exceptions in normal circumstances.
Think of it this way: Giving someone your seed phrase is like giving them your house keys, safe combination, and bank PIN all at once. You wouldn’t do that with your physical assets, so don’t do it with your digital ones.
Use Hardware Wallets for Significant Amounts
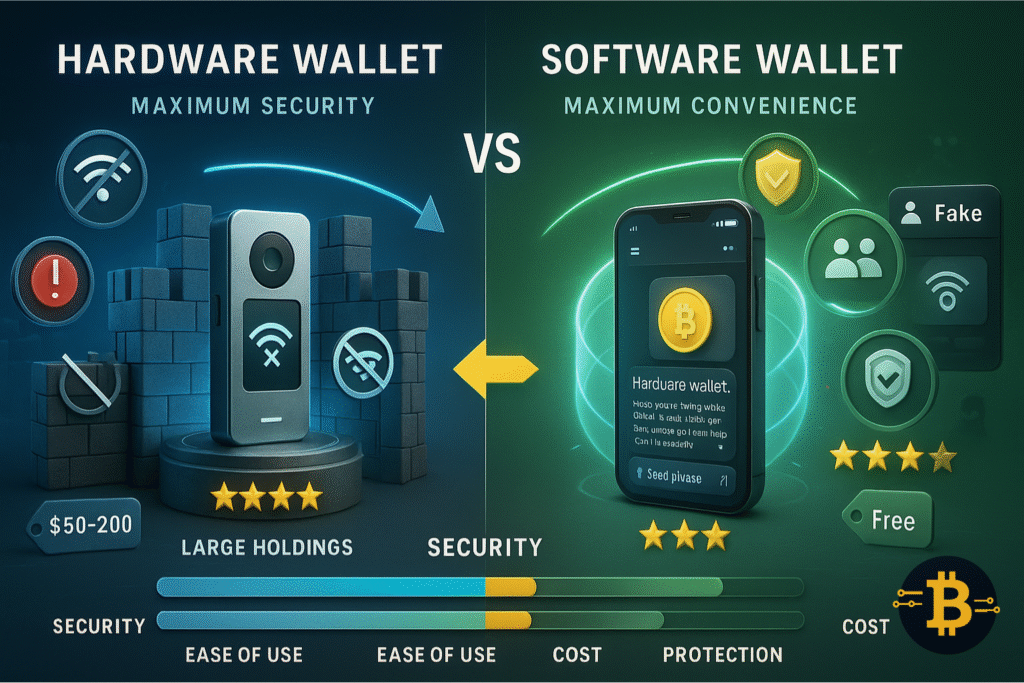
Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor store your private keys on a physical device that never connects directly to the internet. This offline storage protects against malware, phishing, and most online hacking attempts.
Why hardware wallets are safer: Your private keys never leave the device. Even when you connect it to a compromised computer, the signing happens on the hardware wallet itself. Hackers would need physical access to your device to steal your crypto.
When to use one: If you’re holding more than $500-$1,000 in crypto, a hardware wallet is worth the investment. A $100-150 wallet can protect tens of thousands of dollars in assets. For smaller amounts you use frequently, software wallets (like MetaMask or Trust Wallet) offer convenience for daily transactions.
| Security Feature | Software Wallet | Hardware Wallet |
| Private Key Storage | On internet-connected device | Offline, on dedicated device |
| Vulnerability to Malware | High | Very Low |
| Ease of Use | Easy (mobile/desktop app) | Moderate (requires device) |
| Best For | Small amounts, daily use | Large amounts, long-term holding |
| Cost | Free | $50-$200 |
| Examples | MetaMask, Trust Wallet | Ledger, Trezor, SafePal |
Download Wallets from Official Sources Only
The fake wallet app problem is significant and ongoing. Scammers create counterfeit versions of popular wallets and pay for advertisements or SEO to rank them highly in search results. Even official app stores sometimes contain fake apps before they’re identified and removed.
Protection steps:
- Never click on sponsored ads when searching for wallet downloads
- Verify URLs character by character against the official source
- Bookmark official websites for future visits
- Check developer information in app stores (look for official developer name)
- Read recent reviews carefully (sudden negative reviews may indicate an app update introduced malicious code)
In 2022, fake Trust Wallet apps appeared in both the Apple App Store and Google Play Store, stealing funds from hundreds of users before removal. The apps looked professional with stolen branding and fake reviews, making them difficult to distinguish from legitimate versions.
Double-Check Wallet Addresses Every Time
Blockchain transactions are irreversible. Once you send crypto, there’s no “undo” button, no customer service to call, and no way to get it back if you sent it to the wrong address.
Address verification process:
- Copy the recipient’s address
- Paste it into your wallet
- Verify the first 6 characters match
- Verify the last 6 characters match
- For large amounts, send a small test transaction first
Why this matters: Clipboard hijacker malware can change addresses when you paste them. By checking both ends of the address, you catch these attacks. The middle characters are less important because they’re computationally impossible to match while also matching the beginning and end.
For transactions over $1,000, always send a test transaction of $5-10 first. Yes, you’ll pay two transaction fees, but this small cost provides peace of mind and protects against costly mistakes.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds a second verification step beyond your password. Even if a scammer obtains your password through phishing or a data breach, they still can’t access your account without the second factor.
2FA best practices:
- Use authenticator apps (Google Authenticator, Authy, 1Password) rather than SMS
- SMS-based 2FA is vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks
- Enable 2FA on exchanges, email accounts, and any service related to your crypto
- Store backup codes securely (not in cloud storage)
Why SMS 2FA is risky: Scammers can social engineer your mobile carrier into transferring your phone number to their SIM card. Once they control your number, they receive your SMS codes and can access your accounts. Authenticator apps generate codes locally on your device, preventing this attack vector.
Secure Communication: Don’t Trust DMs
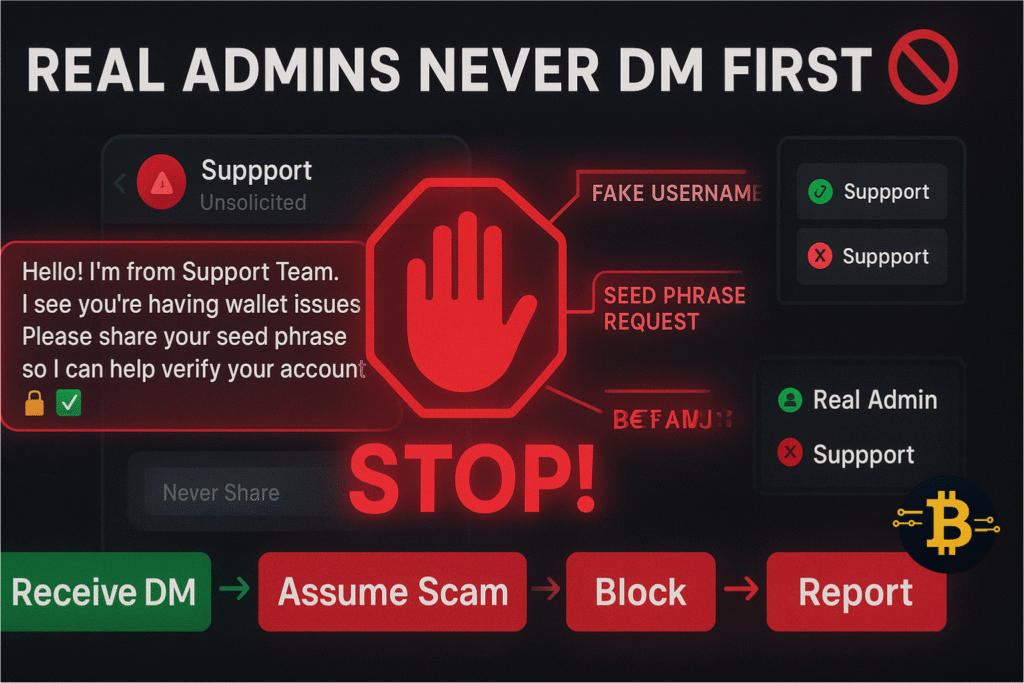
Communication security is just as important as wallet security. Many crypto scams begin with a direct message that seems helpful or legitimate.
The Golden Rule: Admins Never DM First
Here’s a rule that will protect you from countless scams:
Real admins, support teams, and project founders NEVER message you first on Telegram, Discord, WhatsApp, or any platform.
If someone claiming to be support contacts you:
- It’s a scam
- Block and report immediately
- Never share any information
Real support works like this:
- YOU contact THEM through official support channels
- They respond on official platforms (support ticket system, verified email)
- They NEVER ask for your seed phrase, private keys, or password
- They NEVER ask you to connect your wallet or send crypto for “verification”
I’ve seen this scam deployed thousands of times over the years. The scammer watches public channels for people posting problems, then immediately messages them pretending to be support. They seem knowledgeable, use technical language, and appear genuinely helpful – until they ask for your seed phrase or direct you to a malicious website.
How to Verify If Someone Is Real
Verification checklist:
- Check the username carefully (scammers use similar names: “Admin” vs “Adrnin” with a typo)
- Look for official badges or roles in Discord/Telegram
- Ask in the public channel if uncertain: “Is @username official support?”
- Never click links from DMs
- When in doubt, assume it’s fake and verify through official channels
Many crypto projects maintain lists of official team members and their verified account names. Check the project’s website or official social media for this information before trusting any direct message.
Screen Sharing Scams
Never share your screen with strangers, especially regarding crypto-related activities. Scammers use fake “remote assistance” to view your screen while you access your wallet, capturing your seed phrase or password in real-time.
During screen sharing, they can see:
- Your seed phrase if you access it
- Your password as you type it
- Your wallet balances and addresses
- Your email and personal information
Always assume that screen sharing equals theft risk. Legitimate support can help you through written instructions without seeing your screen.
On-Chain Security: Understanding What You’re Signing

Decentralized applications (dApps) require different security awareness than centralized services. When you interact with smart contracts, you’re granting permissions that can have lasting consequences.
The Danger of Blind Signing
When you interact with dApps, you’re often asked to “approve” or “connect your wallet.” These actions grant smart contracts permission to access your tokens. The danger: Malicious contracts can request unlimited spending permissions. Once granted, the scammer can drain your wallet without additional approval.
Always:
- Read what you’re approving carefully
- Check the token amount (is it unlimited or specific?)
- Verify the contract address matches the official one
- Never rush through wallet popup windows
- When unsure, deny permission and research first
Many wallet interfaces now highlight unlimited approvals, but not all do. Look for phrases like “unlimited,” “infinite,” or very large numbers (like 999,999,999,999 tokens). These indicate unlimited permission.
How to Revoke Dangerous Permissions
Even if you’ve already granted permissions to suspicious contracts, you can revoke them. This is essential maintenance that every crypto user should perform regularly.
Tools to check and revoke permissions:
- Revoke.cash (Ethereum, BSC, Polygon)
- Approved.zone (multiple chains)
- Etherscan Token Approvals (Ethereum)
- Your wallet’s built-in approval manager
Steps:
- Visit one of these tools
- Connect your wallet
- Review all active permissions
- Revoke any you don’t recognize
- Revoke permissions for protocols you no longer use
Make this a monthly habit. Old permissions from forgotten dApps can become vulnerabilities if those platforms are later compromised or turn malicious.
Verifying Contract Addresses
One wrong character in a smart contract address means you’re interacting with a completely different – potentially malicious – contract.
How to verify:
- Always get contract addresses from the official project website
- Never trust addresses from social media, Telegram, or unknown websites
- Cross-check on block explorers (Etherscan, BscScan)
- Use CoinGecko or CoinMarketCap for additional verification
- Compare the address character by character
Scammers often create tokens with identical names to legitimate projects. The only way to distinguish them is through the contract address. This verification step takes 30 seconds but can save you from complete loss.
How to Choose Safe Crypto Platforms and Exchanges

Not all crypto platforms offer equal security or legitimacy. Whether you’re choosing an exchange, wallet service, or DeFi protocol, these criteria help you identify trustworthy options.
What to Look For in Crypto Exchanges
Security indicators of safe exchanges:
✅ Regulatory compliance – Licensed and registered with financial authorities (FCA in UK, regulated in US, MAS in Singapore)
✅ Long operational history – Has operated successfully for 3+ years without major security breaches
✅ Cold storage majority – Keeps 95%+ of user funds in offline cold storage, away from internet access
✅ Insurance protection – Offers insurance coverage for digital assets (some exchanges provide FDIC insurance for USD balances)
✅ Two-factor authentication – Requires or strongly encourages 2FA for all user accounts
✅ Withdrawal whitelist option – Allows you to restrict withdrawals to pre-approved addresses only
✅ Transparent reserves – Publishes proof-of-reserves audits (Coinbase and Kraken provide these)
✅ Clear fee structure – Displays all fees transparently with no hidden charges
✅ Responsive support – Provides real customer service that responds within 24-48 hours
✅ Public leadership – Has known founders with real identities and professional reputations
Examples of generally safe exchanges:
- Coinbase (US-based, publicly traded, heavily regulated)
- Kraken (strong security history, proof-of-reserves)
- Binance (largest by volume, though regulatory status varies by country)
- Gemini (US-based, regulated, insured)
Red flags to avoid: ❌ Anonymous team with no verifiable identities ❌ Offshore location with no regulatory oversight ❌ Recent launch (operating less than one year) ❌ History of hacks without user compensation ❌ Unclear security measures ❌ Offers returns significantly above market rates ❌ Poor customer reviews or no reviews at all
DeFi Protocol Safety Checklist
Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms require additional scrutiny because they operate without central oversight.
For DeFi protocols, verify:
- Smart contracts audited by multiple reputable firms
- Open-source code available on GitHub
- Total Value Locked (TVL) over $100 million (indicates community trust)
- Time-tested operation (running 1+ year without exploits)
- Active development team with regular updates
- Bug bounty program incentivizing security researchers
- Clear documentation explaining all features
- Community governance with transparency
Higher TVL generally indicates a protocol has been battle-tested and trusted by the community. However, even established protocols can have vulnerabilities, so never invest more than you can afford to lose.
What to Do If You’ve Been Scammed (Immediate Action Steps)

If you suspect you’ve fallen for a crypto scam, time is critical. While blockchain transactions are irreversible and recovery is difficult, taking immediate action can sometimes limit damage or help authorities track scammers. Here’s exactly what to do.
Step 1: Stop All Interaction Immediately
The moment you realize it’s a scam:
- Stop communicating with the scammer
- Don’t send any more funds (even if they request “taxes” or “fees” to unlock your money—this is a common follow-up scam)
- Don’t follow their instructions to “fix” the situation
- Block them on all platforms
- Save all evidence: screenshots, wallet addresses, conversations, emails, transaction hashes
Scammers often try to extract more money by claiming you need to pay fees, taxes, or verification charges to access your funds. This is always false. Stopping all contact prevents additional losses.
Step 2: Secure Your Remaining Assets
If you still have access to your wallet and remaining funds:
- Immediately transfer any remaining crypto to a new wallet with a new seed phrase
- Revoke all permissions using tools like Revoke.cash
- Change passwords on all crypto-related accounts
- Enable 2FA if you haven’t already
- Scan for malware – run comprehensive antivirus software on your device
- Consider factory reset – if you shared seed phrases or downloaded suspicious files, your device may be compromised
Act fast on this step. If a scammer has access to your wallet or malware on your device, they can drain remaining funds at any moment.
Step 3: Report to Authorities
Report the scam to multiple authorities. While recovery is unlikely, reports help law enforcement track scam operations and potentially prevent future victims.
Where to report:
- FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) – ic3.gov (for US residents)
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) – reportfraud.ftc.gov
- Local cybercrime unit – Most countries have dedicated cybercrime reporting agencies
- The exchange where scam occurred – If the scam happened on a centralized exchange, report immediately
- Blockchain analysis firms – For large-scale scams, companies like Chainalysis sometimes track operations
Information to include in your report:
- Scammer’s wallet address(es)
- All transaction hashes
- Complete communication records (screenshots)
- Detailed timeline of events
- Amount lost (in both crypto and USD value)
- Platform or method used for the scam
- Any identifying information about the scammer
Step 4: Warn Others in the Community
Prevent others from becoming victims by sharing your experience:
- Post warnings on Reddit (r/CryptoCurrency, r/CryptoScams)
- Report to Scam Alert Twitter accounts
- Contact the platform where the scam occurred
- If it was a fake project, report to CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap for delisting
- Share the scammer’s wallet address publicly so others can avoid it
Many community members actively monitor scam reports and can help blacklist addresses or warn potential victims. Your report might save someone else from the same fate.
Can You Recover Crypto from Scammers?
Here’s the honest truth: Recovery is extremely unlikely. Success rates are under 5% for most crypto scam victims.
Blockchain transactions are irreversible by design. Once crypto is sent, it’s gone. However, very rare recovery scenarios exist:
Rare successful recovery cases:
- Centralized exchange freezes scammer’s account before they withdraw (requires very fast action and cooperation)
- Law enforcement seizes scammer assets after investigation (takes months or years, requires large-scale operation)
- Smart contract exploit caught and reversed immediately by protocol developers (extremely rare)
Critical warning about recovery scams: Many scammers target victims a second time, promising to recover lost funds for an upfront fee. This is always a scam. No legitimate service charges fees before recovering funds. If someone contacts you offering recovery services, especially if they found you (rather than you finding them), it’s another scam attempt.
The emotional aftermath of a scam can be devastating. Many victims feel embarrassed, angry, or depressed. Remember: Scammers are professional criminals who spend all day perfecting their tactics. Falling victim doesn’t mean you’re foolish – it means you encountered a skilled criminal. Learn from the experience, implement better security practices, and move forward.
Frequently Asked Questions About Crypto Scams
Can you get scammed on crypto?
Yes, crypto scams are common because blockchain transactions are irreversible and often anonymous. Unlike traditional banking where you can dispute charges or banks can freeze suspicious transactions, crypto offers no such protection. Once you send cryptocurrency to a scammer, it’s gone permanently.
However, understanding common scam types and following security best practices dramatically reduces your risk. Most crypto scam victims could have avoided loss by recognizing basic red flags and following standard security protocols. The technology itself isn’t inherently dangerous – the lack of user education creates vulnerability.
Is crypto full of scams?
While crypto scams exist, they don’t represent the entire industry. Legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges, projects, and use cases far outnumber scams. The perception that “crypto is all scams” comes from media coverage of high-profile frauds and Ponzi schemes.
In reality, millions of people use crypto safely every day for legitimate purposes: international payments, remittances, decentralized finance, and long-term investment. The key is education – understanding how to identify legitimate projects and avoid obvious scams makes crypto as safe as any financial system. Every financial system has fraud; crypto’s transparency actually makes fraud easier to track once identified.
How do I know if a crypto website is legit?
Verify legitimacy through multiple checks:
Technical verification:
- HTTPS encryption and professional design quality
- Domain age (check whois.com – newly created sites are suspicious)
- URL spelling (scammers use similar domains like “coinbas.com”)
Team and project verification:
- Real team members with verifiable backgrounds on LinkedIn
- Active social media with genuine community engagement
- Clear contact information and terms of service
Third-party verification:
- Independent audits or security certifications
- Community reputation (check Reddit, Twitter discussions)
- Listed on reputable aggregators (CoinGecko, CoinMarketCap)
Always compare the URL character-by-character with known official sources. Bookmark legitimate sites rather than searching each time, as scam sites often appear in paid advertisements above legitimate results.
Are crypto giveaways real?
Legitimate crypto giveaways exist but are rare and follow specific patterns. Real giveaways never ask you to send crypto first, never request your seed phrase, and never ask you to “connect your wallet” to claim tokens.
Legitimate giveaways typically require simple social media actions (follow, retweet, comment) with winners selected randomly and announced publicly. The vast majority of crypto giveaways – especially those promising to “double your Bitcoin” or involving celebrity impersonation – are scams.
Golden rule: If you must send money to receive money, it’s always a scam. Real giveaways distribute value freely without requiring payment.
What happens if I give someone my seed phrase?
Giving someone your seed phrase means giving them complete, irreversible control of your crypto wallet. They can recreate your wallet on any device, transfer all your cryptocurrency, and you cannot stop them. Even changing your password afterward won’t help – seed phrases override all other security measures.
If you’ve accidentally shared your seed phrase, immediately create a new wallet with a new seed phrase and transfer all assets before the scammer acts. Consider those funds already stolen and move within minutes, not hours. Every second counts.
Can crypto transactions be reversed if scammed?
No, blockchain transactions cannot be reversed – this is a fundamental feature of cryptocurrency, not a flaw. Once a transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, it’s permanent and cannot be undone by anyone.
This differs dramatically from credit cards or bank transfers where transactions can be disputed or reversed. Extremely rare exceptions exist: if you sent funds to a centralized exchange and caught it before the scammer withdrew, the exchange might freeze the account. Or if a smart contract had an exploitable bug, developers might be able to pause and fix it.
However, in 99% of cases, sent crypto cannot be recovered. This permanence is why prevention is absolutely critical in cryptocurrency security.
How can I tell if a crypto exchange is safe?
Safe exchanges have these characteristics:
Regulatory and operational:
- Licensed and regulated in major jurisdictions
- Operating successfully for 3+ years without major hacks
- Publicly traded or backed by reputable investors
- Clear terms of service and transparent operations
Security features:
- Store 95%+ of funds in offline cold storage
- Offer insurance on digital assets
- Require strong KYC (Know Your Customer) verification
- Provide withdrawal whitelisting and 2FA options
Reputation indicators:
- Real, identifiable leadership team
- Publish proof-of-reserves audits
- Responsive customer support
- High trading volume (indicates market trust)
- Positive long-term community reputation
Examples of generally safe exchanges include Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini, and Binance (though Binance’s regulatory status varies by country). Avoid exchanges promising unusually high interest rates, those without clear regulations, or those with anonymous teams.
What is a rug pull in crypto?
A rug pull occurs when cryptocurrency developers abandon a project and steal investors’ funds. This scam is particularly common in DeFi and new token launches where anyone can create tokens quickly.
How rug pulls work: Scammers create a token with an exciting concept and professional marketing. They build hype through social media, hire influencers for promotion, and attract investment. Once the liquidity pool reaches their target amount (often millions), they suddenly withdraw all liquidity or exploit backdoors in the smart contract. The token’s price crashes to zero and investors cannot sell their holdings.
Protect yourself by checking for: smart contract audits, locked liquidity for extended periods, verified team identities, and code reviews from trusted community members. If a project has anonymous developers and no audit, the rug pull risk is extremely high.
Should I use a hardware wallet?
Yes, if you’re holding more than $500-$1,000 in crypto or plan to hold long-term. Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor store your private keys offline on a physical device, protecting them from malware, phishing, and online hacking attempts.
They cost between $50-$200 but can protect thousands or millions in assets—a small investment for significant security. For smaller amounts or frequent trading, software wallets (MetaMask, Trust Wallet) offer convenience for daily transactions.
General rule: Use hardware wallets for long-term savings (your “crypto bank account”) and software wallets for spending money (your “crypto checking account”). This two-wallet strategy balances security with convenience.
How do I report a crypto scam?
Report crypto scams to multiple agencies to maximize impact:
Reporting agencies:
- FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3.gov) for US residents
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at ReportFraud.ftc.gov
- Your country’s cybercrime unit (most countries have dedicated agencies)
- The platform where the scam occurred (exchange, social media, etc.)
- Blockchain analysis firms for large-scale scams
Evidence to include:
- All scammer wallet addresses
- Transaction hashes (proof of transfers)
- Screenshots of all communications
- Detailed timeline of events
- Amount lost in both crypto and local currency
- Any identifying information
While recovery is unlikely, comprehensive reports help authorities track scam operations, identify patterns, and potentially prevent future victims. Your report contributes to a larger picture that can lead to eventual enforcement action.
Your Crypto Security Checklist: Stay Safe Daily
Security is a habit, not a one-time action. Here’s your daily, weekly, and monthly crypto security checklist to maintain ongoing protection.
Every Day
- Double-check URLs before entering credentials or connecting wallets
- Verify wallet addresses character-by-character before sending funds
- Ignore unsolicited DMs and “support” messages completely
- Question anything that seems too good to be true
- Review any wallet connection requests carefully before approving
Every Week
- Review your wallet transactions for anything unusual or unauthorized
- Check for software and firmware updates on wallets and devices
- Scan devices for malware using updated antivirus software
- Verify your backup and recovery information is secure and accessible
- Stay informed about latest scam tactics in the community
Every Month
- Revoke unused smart contract permissions using tools like Revoke.cash
- Review and update your 2FA settings on all crypto accounts
- Test your backup and recovery process with a small amount
- Educate yourself on new scam types reported in the community
- Verify that all bookmarked crypto sites are still correct and secure
Before Any Investment
- Research the project thoroughly (team, audit, tokenomics, use case)
- Verify all contract addresses from official sources only
- Start with a small test transaction
- Check community sentiment on Reddit, Twitter, and Discord
- Never invest more than you can afford to lose completely
- Take your time – legitimate opportunities don’t require instant decisions
Final Thoughts: Security is a Learnable Skill
You now have comprehensive knowledge on how to avoid crypto scams. You understand the eight common scam types, recognize the psychological tactics scammers use, know the 15 major red flags, and have actionable steps to protect your wallet and investments.
Most importantly, you understand that crypto security isn’t about being paranoid – it’s about being informed. The majority of crypto scams succeed because victims didn’t know what to look for. You do now.
After teaching crypto security for over a decade, I’ve seen thousands of people learn these principles and protect themselves successfully. Security becomes second nature with practice. The habits you build today – double-checking URLs, verifying addresses, questioning promises – will protect you throughout your crypto journey.
Remember: Legitimate opportunities don’t require rushed decisions. When in doubt, slow down and research. Taking an extra hour to verify a project can save you from losing everything. The crypto space offers incredible opportunities, but only for those who approach it with knowledge and caution.
Stay safe, stay informed, and continue learning. The best security system is an educated user who questions everything and verifies independently.
About This Guide
This guide was researched using data from credible sources including government agencies, blockchain analysis firms, and security organizations.
Last Updated: December 2025
Source: Scam examples cited are from publicly reported incidents and verified through multiple sources.
This is educational content only. We do not endorse specific wallets, exchanges, or projects. All examples are for educational purposes. Always do your own research before making financial decisions. This guide does not constitute financial, legal, or investment advice.
Reference
Anyaku, S. (2025, November 30). What is a crypto wallet? Complete guide to types, security & the right one. Cryptogiant –. https://cryptogiant.io/what-is-a-crypto-wallet/
Approved.zone. (2025). Manage your token approvals across chains. Retrieved from https://approved.zone
CertiK. (2025). Blockchain security audits. Retrieved from https://www.certik.com
Chainalysis. (2024). Crypto crime report 2024. Retrieved from https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/crypto-crime-report-2024/
Coinbase. (2025). Cryptocurrency exchange. Retrieved from https://www.coinbase.com
CoinGecko. (2025). Cryptocurrency prices and market data. Retrieved from https://www.coingecko.com
CoinMarketCap. (2025). Cryptocurrency market capitalizations. Retrieved from https://coinmarketcap.com
Etherscan. (2025). Token approvals. Retrieved from https://etherscan.io/tokenapprovalchecker
Federal Bureau of Investigation. (2025). Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3). Retrieved from https://www.ic3.gov
Federal Trade Commission. (2025). Report fraud and scams. Retrieved from https://reportfraud.ftc.gov
Gemini. (2025). Crypto trading and custody platform. Retrieved from https://www.gemini.com
Kraken. (2025). Buy, sell and trade cryptocurrency. Retrieved from https://www.kraken.com
Ledger. (2025). Ledger hardware wallets. Retrieved from https://www.ledger.com
MetaMask. (2025). Ethereum wallet and gateway to blockchain apps. Retrieved from https://metamask.io
OpenZeppelin. (2025). Smart contract security. Retrieved from https://www.openzeppelin.com
Quantstamp. (2025). Smart contract security audits. Retrieved from https://quantstamp.com
Reddit – r/CryptoCurrency. (2025). Retrieved from https://www.reddit.com/r/CryptoCurrency/
Reddit – r/CryptoScams. (2025). Retrieved from https://www.reddit.com/r/CryptoScams/
Revoke.cash. (2025). Revoke token approvals to protect your wallet. Retrieved from https://revoke.cash
Trezor. (2025). Trezor hardware wallets. Retrieved from https://trezor.io
Trust Wallet. (2025). The most trusted crypto wallet. Retrieved from https://trustwallet.com
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. (2025). Investor alerts: Cryptocurrency. Retrieved from https://www.sec.gov/investor/alerts


